By ATS Staff - September 9th, 2020
Computer Languages Python Programming Software Development
Python, a versatile and widely-used programming language, is known for its simplicity and readability. One of the foundational concepts in Python, as in any programming language, is data types. In Python, data types determine the type of value a variable can hold and the operations that can be performed on that value. This article will explore Python's core data types, which are crucial to mastering the language and writing efficient programs.
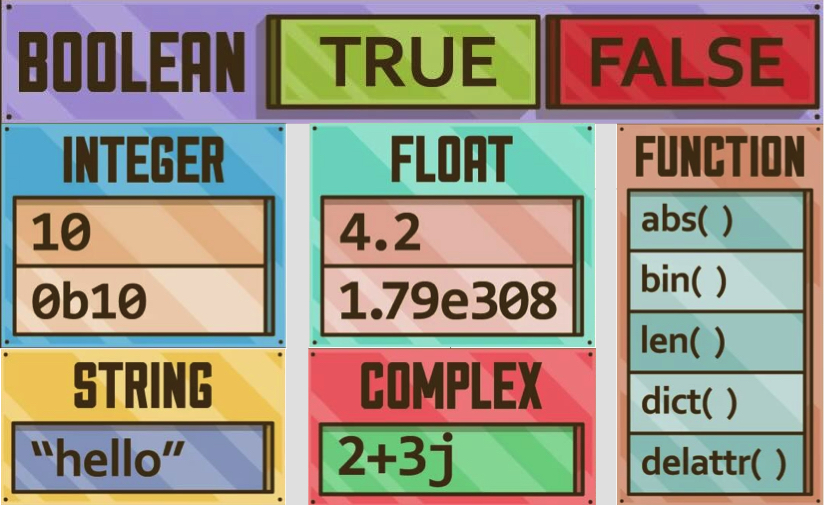
1. Numeric Data Types
Python supports several numeric data types, allowing for various mathematical operations.
- Integers (
int): Whole numbers, positive or negative, without any decimal point.x = 5 y = -10Python handles integers of arbitrary size, meaning you can work with very large numbers without worrying about overflow. - Floating-point numbers (
float): Numbers with a decimal point. Floats are used when dealing with precision values like weights, temperatures, or calculations involving fractions.z = 5.67Python’sfloatis based on the IEEE 754 double-precision standard, ensuring accuracy in most calculations. - Complex numbers (
complex): Python natively supports complex numbers, with a real and imaginary part. They are written asa + bj, whereais the real part andbis the imaginary part.python c = 2 + 3j
2. Sequence Data Types
Sequences are ordered collections of items, and Python provides several types to handle them:
- Strings (
str): Strings are a collection of characters enclosed in single (') or double (") quotes.s = "Hello, Python!"Strings are immutable, meaning once created, they cannot be modified. However, various string operations like concatenation, slicing, and formatting are supported. - Lists (
list): Lists are ordered collections that are mutable, meaning the elements within a list can be changed. Lists can hold elements of different types.my_list = [1, 2, "apple", 3.5]Lists support a variety of operations such as adding, removing, and modifying elements, and slicing to access subsets of the list. - Tuples (
tuple): Similar to lists, but tuples are immutable. Once created, their contents cannot be altered. Tuples are often used to represent fixed collections of items.my_tuple = (1, 2, 3) - Range (
range): A sequence of numbers typically used in loops. It generates a series of numbers within a specified range.python r = range(5) # Generates numbers 0 to 4
3. Set Data Types
Sets are unordered collections of unique elements. Python offers two types of sets:
- Sets (
set): An unordered collection of unique elements. Sets are mutable and allow for operations like union, intersection, and difference.my_set = {1, 2, 3, 4} - Frozen sets (
frozenset): Like sets, but immutable. Once created, you cannot modify the elements of a frozenset.python frozen = frozenset([1, 2, 3])
Sets are useful for operations that require eliminating duplicates or testing membership quickly.
4. Dictionary Data Types
A dictionary (dict) is an unordered collection of key-value pairs. Each key must be unique, but the values can be of any type and may repeat. Dictionaries are mutable, so you can add, remove, or change items after they are created.
my_dict = {'name': 'John', 'age': 25, 'city': 'New York'}
Dictionaries are ideal for representing structured data where quick lookup is required based on unique keys.
5. Boolean Data Type
The boolean data type (bool) represents two values: True and False. It is often used in conditional statements and comparisons.
is_active = True
In Python, boolean values are subclasses of integers, where True is equivalent to 1 and False is equivalent to 0.
6. None Type
Python includes a special type called NoneType, represented by the value None. It signifies the absence of a value and is often used to indicate that a variable has not yet been assigned any value.
value = None
7. Type Conversion
Python allows you to convert between different data types using typecasting functions. Some commonly used type conversion functions are:
int(): Converts a value to an integer.float(): Converts a value to a float.str(): Converts a value to a string.list(): Converts a value to a list.set(): Converts a value to a set.tuple(): Converts a value to a tuple.
Example of typecasting:
x = "123" y = int(x) # Converts string '123' to integer 123
8. Mutable vs Immutable Types
Python data types are either mutable (changeable) or immutable (unchangeable). Understanding this distinction is critical for effective memory management and performance optimization.
- Mutable types: Lists, dictionaries, and sets.
- Immutable types: Integers, floats, strings, tuples, and frozensets.
Conclusion
Python’s built-in data types offer powerful tools for representing and manipulating data. Understanding these core data types is essential for any Python programmer, as they form the foundation of data handling and manipulation in the language. By mastering Python data types, you will be able to write more efficient, readable, and robust code.
Popular Categories
Agile 2 Android 2 Artificial Intelligence 51 Blockchain 2 Cloud Storage 3 Code Editors 2 Computer Languages 12 Cybersecurity 8 Data Science 16 Database 7 Digital Marketing 3 Ecommerce 3 Email Server 2 Finance 2 Google 6 HTML-CSS 2 Industries 6 Infrastructure 3 iOS 3 Javascript 5 Latest Technologies 44 Linux 5 LLMs 11 Machine Learning 32 Mobile 3 MySQL 3 Operating Systems 3 PHP 2 Project Management 3 Python Programming 28 SEO - AEO 5 Software Development 49 Software Testing 3 Web Server 7 Work Ethics 2